How to Secure Caching Managed Database Clusters
Validated on 21 Jul 2021 • Last edited on 16 Apr 2025
Managed Caching is a database engine that supports Redis, an open source, key-value database built with an in-memory design that emphasizes speed. It supports rich data types, atomic operations, and Lua scripting.
Data in Caching database clusters is encrypted at rest with LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) and in transit with SSL. However, there are additional steps you can take to ensure that your data is safe.
Restrict Incoming Connections
You can greatly decrease the likelihood of a security breach by restricting which DigitalOcean resources or external IP addresses are allowed to access the nodes in a cluster. This prevents brute force password and denial-of-service attacks from any server not explicitly permitted to connect.
Typically, only the application servers are allowed to connect to the database cluster. Users access the public-facing site, and the public-facing server authenticates and manages database connections in turn.
Add a Trusted Source Using the CLI
Add a Trusted Source Using the API
Add a Trusted Source using the Control Panel
To restrict access to a database cluster, click the name of the cluster in the control panel to go to its Overview page, then click the Settings tab.
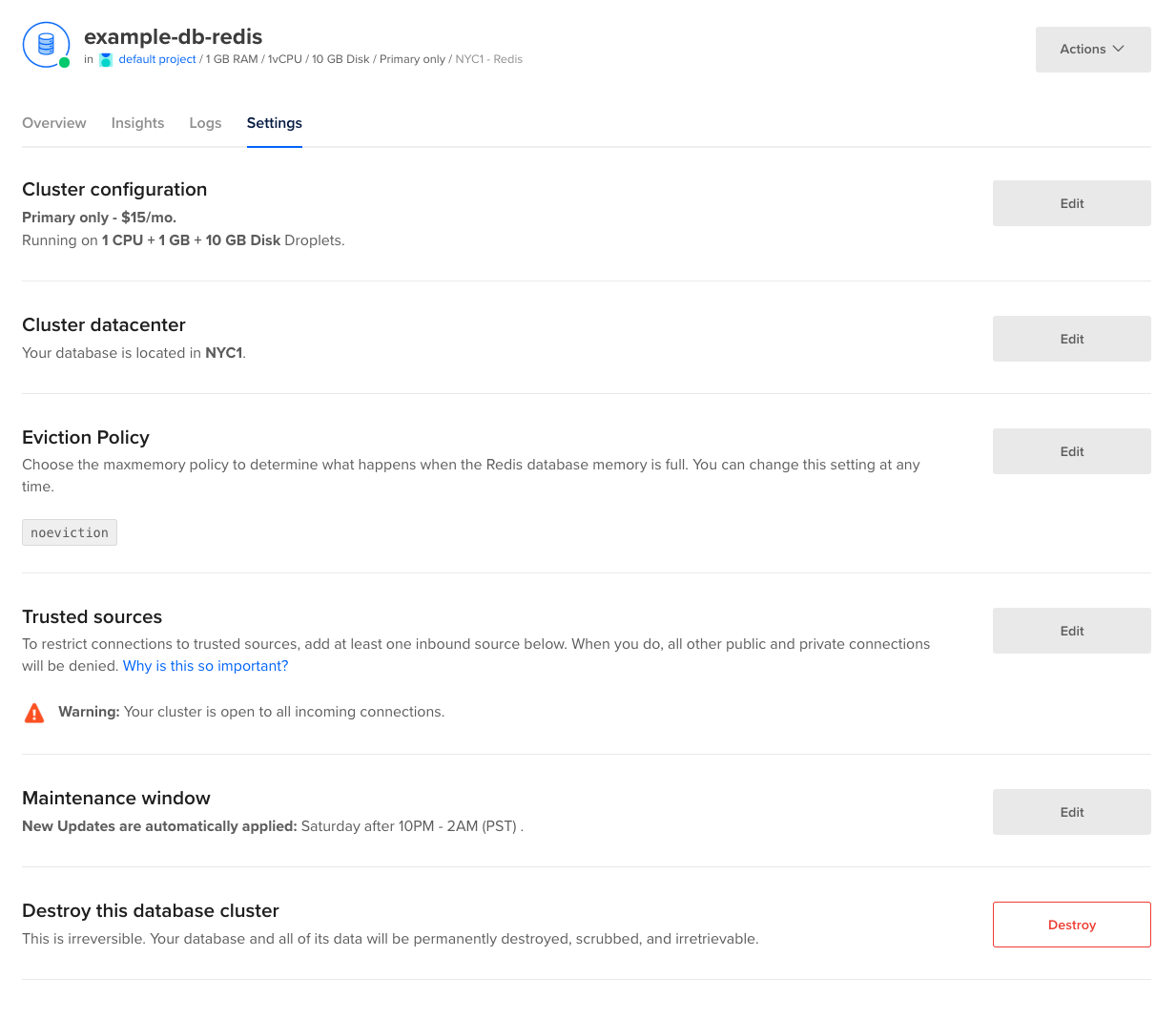
In the section titled Trusted Sources, click Edit to open the Add trusted sources text box.

You can enter Droplets, Kubernetes clusters, tags, apps, or specific IP addresses. Entering a tag provides access to the database for any Droplets or Kubernetes nodes containing that tag. At this time, DigitalOcean Cloud Firewalls are not supported.